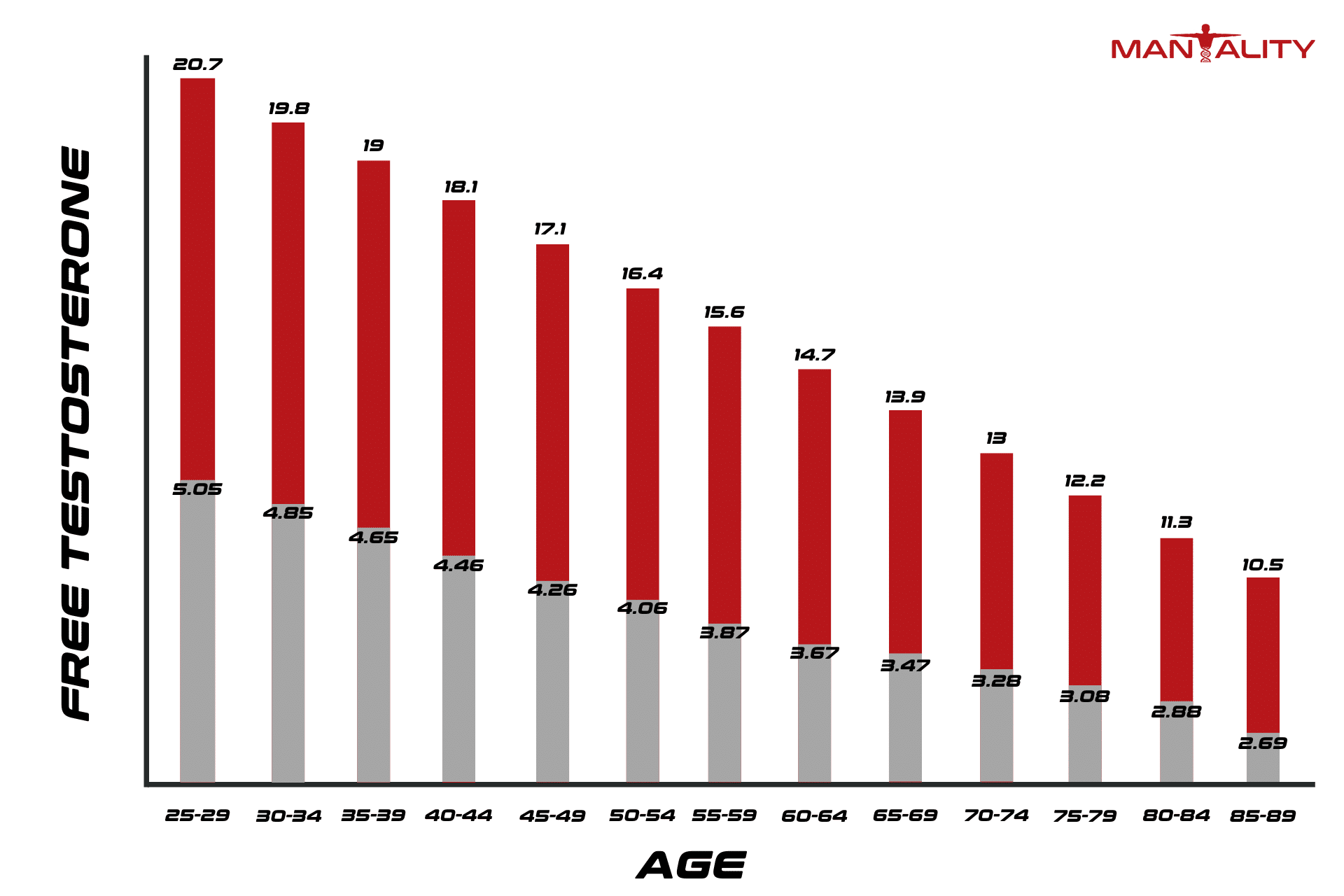
It is estimated that one in every four men over the age of thirty, has a testosterone deficiency.
So you may wonder (and a lot of people do), is testosterone even that important? With the exception of a higher libido, what does testosterone do for men?
The answer as it turns out is quite a bit. Hypogonadism or other testosterone deficiencies are something that affects vital developmental and maintenance functions of the male body. And the older you get, the more likely you are to have a deficiency.
Before we look into the function of testosterone, let’s understand how it is generated.
How Does Your Body Generate Testosterone?
To start things off, we need to go all the way up to the brain. Here the hypothalamus (the decision-maker) analyzes the amount of testosterone your body needs. Accordingly, it puts in a request for the amount it thinks you require.
Then, this message gets passed on to the pituitary gland, which then passes this information on to your testicles.
While your testicles are the main source of testosterone, the adrenal gland adjacent to your kidneys also has the ability to produce small amounts of the hormone when necessary. Testosterone, like other hormones, then travels all through your bloodstream interacting with cells, tissues, and other hormones along the way.
What Does Testosterone Do for Men During Puberty?
The male body begins to produce testosterone very early on in life. Gradually, as a male grows older and nears puberty the amount of testosterone increases.
At this stage, testosterone assists young boys with muscle development, vocal development, or deepening of the voice, increases the growth of body and facial hair and helps in the development of the genitals.
Most young men have adequate levels of testosterone during this period. At this age, if there’s any deficiency, it is probably due to genetic reasons.
Enhancing Fertility
Testosterone is responsible for ensuring the steady production of sperm. That’s why a lot of men with testosterone deficiencies suffer from erectile dysfunction (ED) or impotence and are unable to perform sexually. Men with lower levels tend to have trouble keeping an erection or experiencing one.
This affects the willingness to perform sexually and can cause a decrease in male libido.
Testosterone and the Central Nervous System
Testosterone plays an enormous role in determining male behavior. Aspects like motivation, aggression, competitiveness, enthusiasm, and even confidence are controlled by the amounts of testosterone in the body.
That is why men with lower levels of testosterone may find themselves lacking in energy, feeling lethargic or with a low sense of self-esteem. A low level of testosterone has even been known to cause sleep disturbances and insomnia.
Given the association of testosterone with various emotions, levels of confidence and concentration, it is easy to note the link between testosterone and mental health. That’s why a deficiency can lead to various psychological issues like depression or anxiety.
Stimulates Hair Growth
Most people know that testosterone is a highly important stimulant for facial hair growth during the years of puberty. However, it never really gives up this role. Throughout a man’s life, it remains responsible for hair growth on the arms, legs, underarms and the face.
A decline in testosterone can, therefore, cause thinning of the beard or reduce the overall thickness of a man’s body hair.
Muscle Mass Development
One key function of testosterone is the increase in tissue mass and muscle in the body. It encourages protein synthesis and also interacts with the body’s growth hormones, making it a key determinant of a man’s body mass ratio (BMR).
There are studies that show that men with lower levels of testosterone see higher levels of fat and lower levels of muscle than those with normal hormonal levels. One particular study indicated that muscle growth through resistance training was higher in men with higher levels of testosterone.
However, sometimes sensitivity to the hormone also plays a role in how it stimulates muscle growth.
Muscle cells have androgen receptors that are responsible for interacting with testosterone. When testosterone comes in contact with these receptors, more muscle mass is maintained.
However, there are still some ways you could build muscle mass with low testosterone. A commitment to strength training and aerobic exercises, good sleep, and a well-balanced, healthy diet can all assist you in developing a fitter physique. If all else fails, you can also consider hormone replacement therapy.
Immunity and Inflammation
Low testosterone levels also increase the risk of chronic inflammation. Simultaneously it increases the risk of other immunity-related diseases like metabolic syndrome. This, in turn, can increase one’s risks for heart disease and even strokes.
Given that it helps men burn fat and maintain a healthy metabolic rate, a deficiency can also cause weight gain, poor mobility, and fatigue.
Bone Density
With lowered testosterone also comes lowered bone density. There have been several studies that show a link between testosterone deficiencies and osteoporosis in men. This has been noted even in younger men and isn’t limited to older men as was previously thought.
In a nutshell, low levels of testosterone cause bone cells to regenerate far too quickly. This makes them fragile and more susceptible to fractures and breaks.
An increase in testosterone can help improve conditions like anemia, arthritis, and osteoporosis. Most physicians suggest changes in diet and lifestyle and testosterone replacement therapy. Many patients have seen improvements in their bone density after being put on hormone replacement.
A recent study even showed that these effects were particularly beneficial for men with type 2 diabetes and another showed they were also beneficial for those with HIV.
The Circulatory System
Testosterone is also responsible for interacting with bone marrow in order to trigger the production of red blood cells. It may also cause changes to the levels of cholesterol, however, studies have been mostly inconclusive in that regard.
Lower Testosterone = Higher Risk for Diabetes, Obesity, and Hypertension, or Vice Versa
There is a definite link between low levels of testosterone and diabetes. The two often co-exist in the same person. Men with a testosterone deficiency are more likely to develop diabetes in later stages.
Additionally, men with diabetes often have a testosterone deficiency.
The reason for this link is that testosterone enables the body to take in more blood sugar when interacting with the hormone insulin.
In a similar way, the deficiency is also linked to obesity and weight gain. Fat cells in obese men can interact with testosterone to convert it into estrogen, thereby exacerbating their deficiency.
Obesity and diabetes are directly linked to higher blood pressure.
Symptoms of Low Testosterone
Symptoms of deficiencies manifest differently in adult men. Factors like obesity, diabetes, and hypertension can increase one’s chances of having a deficiency. During the later years of manhood, if the deficiency kicks in, men may begin to notice symptoms like:
- Loss of energy or fatigue
- A decrease in muscle mass
- A lower bone mass density
- A decrease in overall sex drive, or libido
- Erectile dysfunction
- High blood sugar levels
- Excess weight gain
- Thining of facial or body hair
- Low mood or depression
- Poor concentration
Symptoms like these indicate that the body is not receiving sufficient levels of testosterone.
What Are the Causes of a Testosterone Deficiency?
Well, it could be because of injury to your testicles or due to a hormonal disorder.
Treatments that include radiation therapy, genetic roots, poor levels of vitamin D and zinc, a high level of iron and a damaged pituitary gland are also associated with this hormonal deficiency. However, sometimes it may have to do with external medications or enhancers. Excessive use of steroids, in particular, and similar supplements, have been known to disrupt the production of testosterone in the body.
What You Can Do to Treat Low Levels of Testosterone
So now that we’ve gone through the various ways testosterone helps you function, let’s look into what you can do to prevent or treat a deficiency. Here are four of the main changes you can incorporate into your life.
A Change in Diet
If you are overweight, a change in diet can help you lose weight, and consequently improve your hormonal levels. However, there are also some dietary changes that will help stimulate the production of testosterone. Vitamin D and zinc are both, key elements in the production of testosterone.
Consider incorporating foods like tuna, sardines, and low-fat milk fortified with sources of vitamin D.
Other good foods include eggs, oysters, ginger, pomegranates, leafy greens, shellfish, beef, and kidney beans. Do keep in mind that moderation and balance are the keys to a healthy, nutritious diet. If your vitamin D levels are really low, consult your doctor on whether vitamin supplements are right for you.
This is particularly true for shellfish, oysters, and seafood. These tend to have small amounts of mercury that can be dangerous to the body in higher quantities. Try to restrict yourself to around three portions of seafood per week to maintain a good balance.
Lifestyle Changes You Can Make
Consider incorporating some resistance training and high-intensity interval training (HIIT) into your exercise routines. HIIT, in particular, has proven to be more effective in boosting testosterone levels than steady-state cardio.
Also, do review any medication or treatment you might be on. Sometimes the interaction of certain medications with your body can prevent or inhibit the production of hormones.
Spending more time outdoors in the sunshine helps your body generate more vitamin D.
A fun way to do this could be to schedule regular hiking, expeditions, trekking, cycling or walking to get the benefits of exercising as well as vitamin D.
And finally, make sure you get a good night’s sleep of at least 7-9 hours every day. Sleep plays a vital role in determining the quality of your overall health and is especially important if you’re getting regular exercise.
What Medical Treatments Are Available?
Medical treatments must be prescribed by a certified physician or doctor. These could include testosterone patches, topical gels, pills or even injections. Hormone replacement therapy is extremely effective. But, like any other medical treatment, it does come with a few risks.
Make sure you report any strange feelings, rashes or suspicious changes to your doctor.
Getting a Diagnosis
If you suspect that you may have a deficiency do get a physical exam and a blood test done with your physician. If you are above the age of 30, you should definitely make regular checks, given that you are at higher risk for a deficiency. Your levels may fluctuate throughout the day, but it will be at its highest during the morning.
300-1070ng/dL are considered normal levels in an adult male. A man whose levels are lower than 300ng/dL might qualify for hormone replacement therapy.
Where Can You Get Testosterone Replacement Therapy?
There you go. If you were wondering—what does testosterone do for men? Well, now you know. So if you do have a deficiency you should definitely consider hormone replacement therapy.
Make sure you get this done at a qualified clinic under the care of the appropriate medical staff. Be wary of shady advertisements online with outlandish promises and unrealistic results. Make sure you do sufficient research before choosing a place, have a look at reviews and visit the place to make sure you are getting your money’s worth.
Got more questions about testosterone replacement therapy? Check out our list of FAQs where we’ve answered some of the most common questions about it so that you know exactly what to expect.